Organizations face growing pressure to reskill employees at speed while supporting hybrid workforces and diverse learning needs. Classroom training alone cannot scale, and digital-only learning often lacks the engagement required to drive real performance change. Blended learning, which combines the reach of digital programs with the impact of face-to-face instruction, offers a proven way to close skills gaps and deliver measurable results. The market reflects this shift: it grew from USD 21.09 billion in 2024 to USD 23.25 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 37.51 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 10.07% according to Business Research Insights.
In this article, we define blended learning, explore its models and benefits, outline the challenges, and demonstrate how Whatfix helps enterprises achieve business impact through blended learning.
Here are the five most common types of blended learning frameworks:
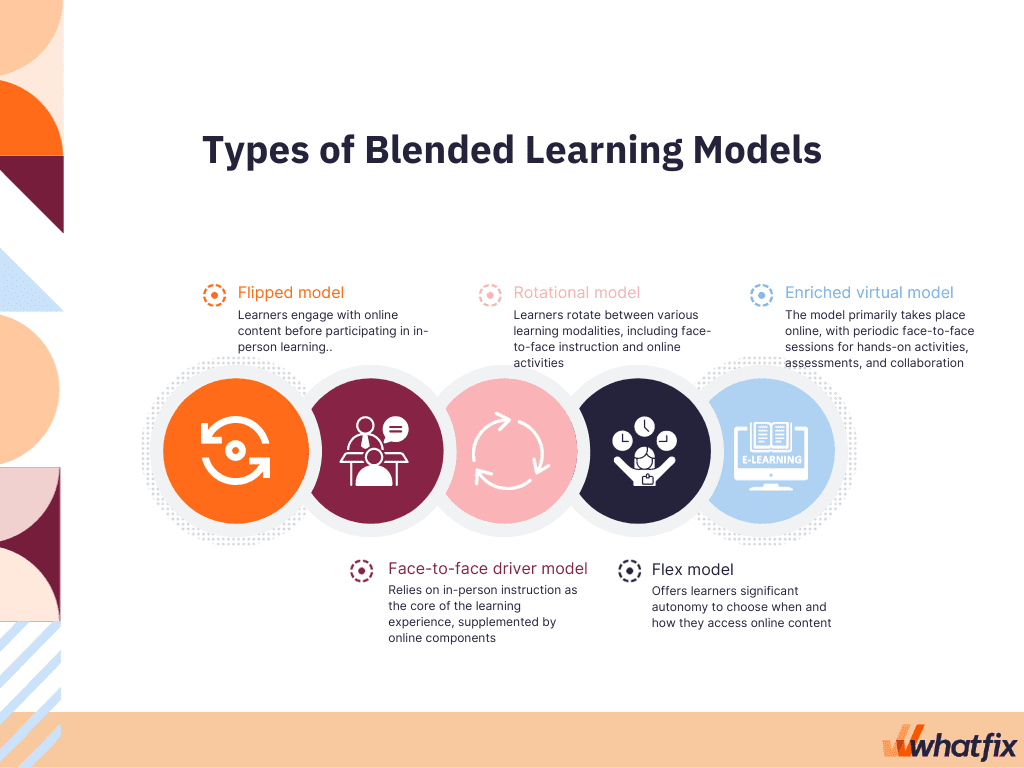
- Flipped model: In the flipped model, traditional classroom instruction is inverted. Learners first encounter the instructional content outside of class, typically through video lectures, readings, or online modules. Then, in-class time is dedicated to active learning activities, discussions, group projects, and exercises that reinforce and apply the pre-learned material. The flipped model allows for more personalized learning during face-to-face sessions and provides students with the flexibility to learn at their own pace.
- Face-to-face driver model: The face-to-face driver blended learning model is the closest to traditional classroom training, as most of the training takes place in a classroom setting under the guidance of an instructor. This approach offers individual, personalized support to learners who are struggling to grab the new concepts or are falling behind the training curriculum.
- Rotational model|: In the rotational model, learners rotate between different learning modalities, such as face-to-face instruction, online activities, small-group discussions, and independent study. These rotations can be on a fixed schedule (e.g., daily or weekly) or based on learners’ progress. It offers flexibility and caters to various learning styles, allowing employees to work in the modality that best suits their needs at a particular time.
- Flex model: The flex model gives learners significant autonomy and control over their learning path. It combines online learning with in-person support as needed. Using an adaptive learning platform, learners can choose when and where they access online content and resources, making it suitable for self-paced learning. Instructors can assist learners when required, helping them navigate the material and address any challenges.
- Enriched virtual model: The enriched virtual model is primarily an online learning experience with periodic face-to-face sessions. Most of the learning occurs in a virtual environment, but learners attend physical classes or workshops at designated times for hands-on activities, assessments, or collaborative projects. This model combines the flexibility of online learning with the benefits of in-person interaction, ensuring learners receive individualized instruction and group engagement opportunities.
How to Create a Blended Learning Program
Building an effective blended learning program requires a structured approach that balances business goals, learner needs, and the right mix of delivery methods.
1. Define Training Objectives
Start by setting clear training objectives. These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals). Identify the skills or competencies employees need to develop, and determine what success looks like in terms of performance outcomes.
2. Select the Blended Learning Model
Choose the blended learning model that best fits your objectives, audience, and resources. Options include flipped classroom, rotational, flex, face-to-face, or enriched virtual models. Each combines digital and in-person elements differently, so align the choice with your organizational context.
3. Choose Delivery Methods
Blend delivery methods to match your goals and workforce needs:
- eLearning modules for self-paced flexibility
- Live virtual training for real-time interaction across dispersed teams
- In-person workshops for collaboration, hands-on training, and team building
- Mobile learning for on-the-go accessibility
- Simulations and role-play for risk-free practice of real-world scenarios
4. Leverage the Right Learning Tools
Technology is central to delivering and scaling blended learning. Core tools include:
- Learning Management System (LMS): for content management, tracking, and reporting.
- Digital Adoption Platform (DAP): for in-app guidance and workflow support that reinforces learning in the flow of work.
- Sandbox environments: for safe practice and skill application in simulated systems.
5. Assess and Evaluate Effectiveness
Use assessments such as quizzes, simulations, and performance reviews to measure knowledge transfer and application. Track metrics like completion rates, learner engagement, and time-to-proficiency. Link these measures back to business objectives to demonstrate ROI.
6. Collect Feedback and Iterate
Gather feedback from learners to understand their experience and challenges. Use insights to refine the program design, update content, and adjust delivery methods. Continuous improvement ensures the blended program remains relevant, effective, and aligned with business needs.
Common Challenges in Blended Learning
Even with clear benefits, blended learning can be difficult to implement at scale. Organizations often face these hurdles:
- Technology adoption and technical issues: Employees may struggle to adapt to new digital platforms or tools. Connectivity issues, software glitches, and lack of familiarity with learning technologies can slow adoption and reduce program effectiveness.
- Management and scheduling complexity: Coordinating online and in-person elements requires significant planning. Administrators must ensure learners complete digital modules before workshops, and instructors need visibility into learner progress to personalize sessions.
- Delayed feedback and learner support: In self-paced modules, learners often miss the real-time guidance they would receive in a classroom. Questions may go unanswered until follow-up sessions, creating frustration and slowing skill development.
- Content integration across formats: Digital and in-person elements can feel disconnected if not carefully aligned. Learners need to see a clear link between what they practice online and what they apply in the classroom or on the job.
- Tracking and measuring success: With activities spread across multiple tools and environments, it becomes difficult to get a unified view of learner engagement, learning retention, and business impact. Without the right data, proving ROI is a challenge for L&D leaders.
8 Examples of Blended Learning for Employee Training
Enterprises stuck in rigid training cycles lose momentum fast. Blended learning breaks that pattern by combining formats that move employees forward with fewer delays and far better knowledge retention. The following examples are the most practical, high-leverage models for modern workplace learning and should form the backbone of any serious L&D program.
1. Live Instructor-Led Training + Digital Adoption Flows
Workshops create alignment, but they rarely change behavior on their own. When employees return to the application days later, most of the instructions have evaporated. Combining live sessions with Whatfix Flows fixes that gap. Instructors introduce the concepts, then learners practice in the actual system with step-by-step, contextual guidance. This method converts theoretical understanding into muscle memory, eliminating the typical post-training confusion that hinders productivity.

2. Microlearning Videos + In-App Smart Tips
Short-form content delivers clarity without draining attention. Pairing these videos with in-app Smart Tips turns every workflow into a supported experience. Learners absorb the “what” in the video and the “how” inside the interface at the moment of action. It drives consistent task execution and eliminates the outdated expectation that employees should memorize every step.
3. Virtual Classrooms + Hands-On Sandbox Environments
Virtual training scales, but it often lacks real practice. Providing learners with a sandbox environment immediately after the session creates a controlled space to test workflows without incurring production risk. Employees sharpen their skills through experimentation, which accelerates their confidence and reduces their dependence on administrators or power users.
4. Scenario-Based E-Learning + Live Peer Review
Scenario-based modules create realism, but employees need external input to challenge their assumptions. Peer review exposes blind spots early and strengthens judgment. Teams that adopt this model build stronger problem-solving instincts and develop a culture where feedback becomes normal rather than reserved for performance reviews.
5. Knowledge Base Content + Whatfix Self Help
Long-form documentation gives depth, yet employees rarely dig through it during real work. With Whatfix Self Help, that same content appears contextually based on the task, the user’s role, or the page they’re on. Employees stop guessing, and support queues shrink because guidance becomes instantly accessible without opening a new tab.
6. Job Shadowing + Digital Checklists
Shadowing grants exposure but fails when learners try the task alone days later. Digital checklists reinforce the steps and bring order to the learner’s first independent attempts. Operations teams, field technicians, and service roles benefit most because errors drop and consistency rises quickly.
7. Compliance Courses + In-App Process Validation
Compliance programs collapse when they rely only on annual courses. In-app validation fixes this outdated model. Employees complete required learning, then the system confirms they follow the required workflow inside the application. This creates a measurable record of behavior, not just attendance, strengthening audit readiness and reducing compliance drift.
8. LMS Learning Paths + Continuous In-App Nudges
LMS modules create structure, but the learning decays without reinforcement. In-app nudges reactivate knowledge at key workflow moments, especially during the first 30-60 days after training. This hybrid model strengthens retention and ensures new skills don’t fade once the learner finishes the LMS track.
Modernize Your User Training Approach With Whatfix
A high-performing learning strategy treats training as a living system, not a one-time event. Organizations that rely on static materials or disconnected tools end up with uneven adoption, inconsistent workflows, and a workforce that learns slower than the pace of change. Whatfix eliminates that drag by pairing real-time, in-app guidance with experiential learning environments that prepare employees for actual work, not a theoretical version of it.
Mirror advances this advantage even further. Teams can create safe, accurate replicas of enterprise applications within seconds, allowing employees to practice new workflows without production risk. This transforms blended learning from a content-heavy program into a hands-on engine for mastery. Employees build confidence as they navigate complex processes in a controlled environment, and leaders gain visibility into where individuals struggle before those gaps become operational problems.
Once training shifts from classroom or LMS into the actual application, Whatfix’s Digital Adoption Platform takes over. Flows, Smart Tips, Pop-Ups, and Self Help reinforce every lesson directly in the workflow. Mirror prepares employees. DAP embeds the behavior. Together they turn new knowledge into consistent execution, cut support volumes, and reduce the time required for users to reach full productivity.
Enterprises that align learning and adoption with a unified Whatfix stack see measurable revenue protection, stronger compliance, and faster transformation cycles. This approach creates a workforce that adapts quickly, applies new skills accurately, and delivers predictable results across every function. It positions training as a strategic accelerator, not a cost center, and sets the organization up for sustained performance in an environment defined by continuous change.
Request a Whatfix demo