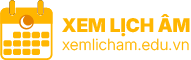1,2-Dichloroethane
Names Preferred IUPAC name Other names Identifiers 605264 ChEBI ChEMBL ChemSpider DrugBank ECHA InfoCard 100.003.145 EC Number 49272 KEGG RTECS number UNII Properties C2H4Cl2 Molar mass 98.95 g·mol−1 Appearance Colorless liquid Odor characteristic, pleasant chloroform-like odor[2] Density 1.253 g/cm3, liquid Melting point −35 °C (−31 °F; 238 K) Boiling point 84 °C (183 °F; 357 K) 0.87 g/100 mL (20 °C) Viscosity 0.84 mPa·s at 20 °C Structure 1.80 D Hazards Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): Toxic, flammable, possibly carcinogenic GHS labelling: Danger H225, H302, H315, H319, H335, H350 P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 NFPA 704 (fire diamond) Flash point 13 °C (55 °F; 286 K) Explosive limits 6.2-16%[2] Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): 3000 ppm (guinea pig, 7 h)1000 ppm (rat, 7 h)[3] 1217 ppm (mouse, 2 h)1000 ppm (rat, 4 h)3000 ppm (rabbit, 7 h)[3] NIOSH (US health exposure limits): TWA 50 ppm C 100 ppm 200 ppm [5-minute maximum peak in any 3 hours][2] Ca TWA 1 ppm (4 mg/m3) ST 2 ppm (8 mg/m3)[2] Ca [50 ppm][2] Related compounds Methyl chlorideMethylene chloride1,1,1-Trichloroethane Ethylene1,1-DichloroethaneVinyl chloride Supplementary data page 1,2-Dichloroethane (data page)
The chemical compound 1,2-dichloroethane, commonly known as ethylene dichloride (EDC), is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colourless liquid with a chloroform-like odour. The most common use of 1,2-dichloroethane is in the production of vinyl chloride, which is used to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, furniture and automobile upholstery, wall coverings, housewares, and automobile parts.[4] 1,2-Dichloroethane is also used generally as an intermediate for other organic chemical compounds, and as a solvent. It forms azeotropes with many other solvents, including water (at a boiling point of 70.5 °C or 158.9 °F or 343.6 K) and other chlorocarbons.[5]
In 1794, physician Jan Rudolph Deiman, merchant Adriaan Paets van Troostwijk, chemist Anthoni Lauwerenburg, and botanist Nicolaas Bondt, under the name of Society of Dutch Chemists (Dutch: Gezelschap der Hollandsche Scheikundigen), were the first to produce 1,2-dichloroethane from olefiant gas (oil-making gas, ethylene) and chlorine gas.[6] Although the Gezelschap in practice did not do much in-depth scientific research, they and their publications were highly regarded. Part of that acknowledgement is that 1,2-dichloroethane was called “Dutch oil” in old chemistry. This is also the origin of the archaic term “olefiant gas” (oil-making gas) for ethylene, for in this reaction it is ethylene that makes the Dutch oil. “Olefiant gas” is the etymological origin of the modern term “olefins”, the family of hydrocarbons of which ethylene is the first member.
Nearly 20 million tons of 1,2-dichloroethane are produced annually in the United States, Western Europe, and Japan.[7] Production is primarily achieved through the iron(III) chloride-catalysed reaction of ethylene and chlorine:
H2C=CH2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → ClC2H4Cl (l) (ΔH⊖r = −218 kJ/mol)
1,2-dichloroethane is also generated by the copper(II) chloride-catalysed oxychlorination of ethylene:
H2C=CH2 + 2 HCl + 1/2 O2 → ClC2H4Cl + H2O
Approximately 95% of the world’s production of 1,2-dichloroethane is used in the production of vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) with hydrogen chloride as a byproduct. VCM is the precursor to polyvinyl chloride.
ClC2H4Cl → H2C=CHCl + HCl
The hydrogen chloride can be re-used in the production of more 1,2-dichloroethane via the oxychlorination route described above.[8]
1,2-Dichloroethane has been used as degreaser and paint remover but this use has phased out due to its toxicity. As a useful ‘building block’ reagent, it is used as an intermediate in the production of diverse organic compounds such as ethylenediamine and higher ethyleneamines.[9] In the laboratory it is occasionally used as a source of chlorine, with elimination of ethene and chloride.
Via several steps, 1,2-dichloroethane is a precursor to 1,1,1-trichloroethane. Historically, before leaded petrol was phased out, chloroethanes were used as an additive in petrol to prevent lead buildup in engines.[10]
1,2-Dichloroethane is highly flammable[11] and releases hydrochloric acid when combusted:
ClC2H4Cl + 5/2 O2 → 2 CO2 + H2O + 2 HCl
It is also toxic (especially by inhalation due to its high vapour pressure) and possibly carcinogenic. Its high solubility and 50-year half-life in anoxic aquifers make it a perennial pollutant and health risk that is very expensive to treat conventionally, requiring a method of bioremediation.[12] While the chemical is not used in consumer products manufactured in the U.S., a case was reported in 2009 of molded plastic consumer products (toys and holiday decorations) from China that released 1,2-dichloroethane into homes at levels high enough to produce cancer risk.[13][14]
Substitutes are recommended and will vary according to application. Dioxolane and toluene are possible substitutes as solvents. Dichloroethane is unstable in the presence of aluminium and, when moist, with zinc and iron.[citation needed]
- Gezelschap der Hollandsche Scheikundigen
- ChemicalLand compound database
- Environmental Chemistry compound database
- Merck Chemicals database
- National Pollutant Inventory – 1,2 Dichlorethane Fact Sheet
- Locating and estimating air emissions from sources of ethylene dichloride, EPA report EPA-450/4-84-007d, March 1984